- Drivers Marvell Port Devices Lucie
- Drivers Marvell Port Devices Replicator
- Drivers Marvell Port Devices Gigabit
However, serial bus controller in Device Manager contains USB devices and USB port numbers and it seems COM Ports devices might be hidden, so please follow the steps mentioned below and check if you can see the Com Ports. Open Device Manager. Click on View in the menu bar and select Show hidden devices. Locate Ports (COM & LPT) in the list. Driver Downloads. Download the latest Marvell drivers for your specific device or application.
This is a Windows 10 WHQL certified driver, which is not provided by default on some systems, for Windows 10, including the X58A chipset and other older Intel chipset motherboards. This will upgrade the SATA3 Controller from Marvell, on your motherboard, to the latest Windows 10 drivers. These drivers, for whatever reason, are also not on the Marvell website. Instructions:
Instructions: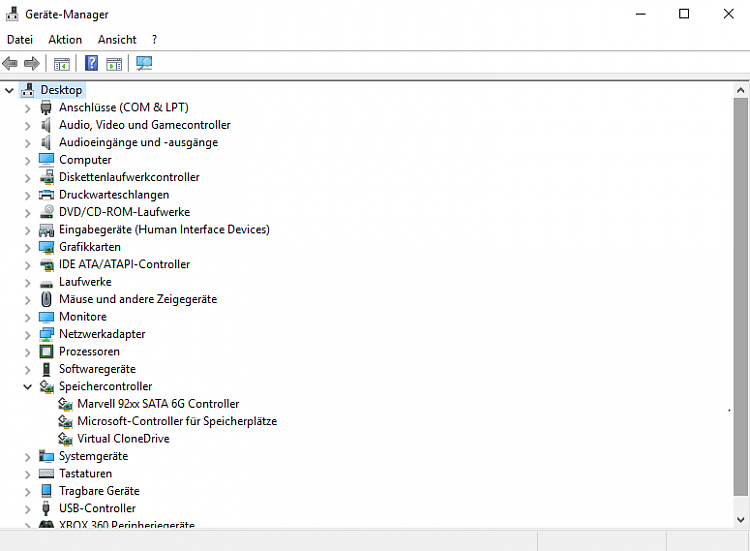
- Extract the entire contents of Marvell_SATA_V1.2.0.1047.zip to a folder (Downloads being the most likely choice)
- Launch Device Manager by typing 'devmgmt.msc' (without quotations) into Search.
- Go to Storage Controller and identify your Marvell 91xx controller driver.
- Right-click on this device and click 'Update driver software'.
- Choose 'Browse my computer for driver software'.
- Navigate or enter %USERPROFILEDownloadsMarvell_SATA_V1.2.0.1047
- Your device driver will be updated and you will be prompted to reboot.
Copyright (c) 2020 Marvell International Ltd.
Contents¶
Overview¶
Resource virtualization unit (RVU) on Marvell’s OcteonTX2 SOC maps HWresources from the network, crypto and other functional blocks intoPCI-compatible physical and virtual functions. Each functional blockagain has multiple local functions (LFs) for provisioning to PCI devices.RVU supports multiple PCIe SRIOV physical functions (PFs) and virtualfunctions (VFs). PF0 is called the administrative / admin function (AF)and has privileges to provision RVU functional block’s LFs to each of thePF/VF.
- Network pool or buffer allocator (NPA)
- Network interface controller (NIX)
- Network parser CAM (NPC)
- Schedule/Synchronize/Order unit (SSO)
- Loopback interface (LBK)
- Crypto accelerator (CPT)
- Scheduled timers unit (TIM)
- Schedule/Synchronize/Order unit (SSO)Used for both networking and non networking usecases
- A PF/VF with NIX-LF & NPA-LF resources works as a pure network device
- A PF/VF with CPT-LF resource works as a pure crypto offload device.
RVU functional blocks are highly configurable as per software requirements.
- Enables required number of RVU PFs based on number of physical links.
- Number of VFs per PF are either static or configurable at compile time.Based on config, firmware assigns VFs to each of the PFs.
- Also assigns MSIX vectors to each of PF and VFs.
- These are not changed after kernel boot.
Drivers¶
Linux kernel will have multiple drivers registering to different PF and VFsof RVU. Wrt networking there will be 3 flavours of drivers.
Admin Function driver¶
As mentioned above RVU PF0 is called the admin function (AF), this driversupports resource provisioning and configuration of functional blocks.Doesn’t handle any I/O. It sets up few basic stuff but most of thefuncionality is achieved via configuration requests from PFs and VFs.
PF/VFs communicates with AF via a shared memory region (mailbox). Uponreceiving requests AF does resource provisioning and other HW configuration.AF is always attached to host kernel, but PFs and their VFs may be used by hostkernel itself, or attached to VMs or to userspace applications likeDPDK etc. So AF has to handle provisioning/configuration requests sentby any device from any domain.
- Manage physical ethernet links ie CGX LMACs.
- Retrieve information like speed, duplex, autoneg etc
- Retrieve PHY EEPROM and stats.
- Configure FEC, PAM modes
- etc
- Map a physical link to a RVU PF to which a netdev is registered.
- Attach NIX and NPA block LFs to RVU PF/VF which provide buffer pools, RQs, SQsfor regular networking functionality.
- Flow control (pause frames) enable/disable/config.
- HW PTP timestamping related config.
- NPC parser profile config, basically how to parse pkt and what info to extract.
- NPC extract profile config, what to extract from the pkt to match data in MCAM entries.
- Manage NPC MCAM entries, upon request can frame and install requested packet forwarding rules.
- Defines receive side scaling (RSS) algorithms.
- Defines segmentation offload algorithms (eg TSO)
- VLAN stripping, capture and insertion config.
- SSO and TIM blocks config which provide packet scheduling support.
- Debugfs support, to check current resource provising, current status ofNPA pools, NIX RQ, SQ and CQs, various stats etc which helps in debugging issues.
- And many more.
Physical Function driver¶
This RVU PF handles IO, is mapped to a physical ethernet link and thisdriver registers a netdev. This supports SR-IOV. As said above this drivercommunicates with AF with a mailbox. To retrieve information from physicallinks this driver talks to AF and AF gets that info from firmware and respondsback ie cannot talk to firmware directly.
Supports ethtool for configuring links, RSS, queue count, queue size,flow control, ntuple filters, dump PHY EEPROM, config FEC etc.
Virtual Function driver¶
There are two types VFs, VFs that share the physical link with their parentSR-IOV PF and the VFs which work in pairs using internal HW loopback channels (LBK).
- These VFs and their parent PF share a physical link and used for outside communication.
- VFs cannot communicate with AF directly, they send mbox message to PF and PFforwards that to AF. AF after processing, responds back to PF and PF forwardsthe reply to VF.
- From functionality point of view there is no difference between PF and VF as same typeHW resources are attached to both. But user would be able to configure few stuff onlyfrom PF as PF is treated as owner/admin of the link.
Drivers Marvell Port Devices Lucie
- RVU PF0 ie admin function creates these VFs and maps them to loopback block’s channels.
- A set of two VFs (VF0 & VF1, VF2 & VF3 .. so on) works as a pair ie pkts sent out ofVF0 will be received by VF1 and viceversa.
- These VFs can be used by applications or virtual machines to communicate between themwithout sending traffic outside. There is no switch present in HW, hence the supportfor loopback VFs.
- These communicate directly with AF (PF0) via mbox.
Except for the IO channels or links used for packet reception and transmission there isno other difference between these VF types. AF driver takes care of IO channel mapping,hence same VF driver works for both types of devices.
Basic packet flow¶
Ingress¶
- CGX LMAC receives packet.
- Forwards the packet to the NIX block.
- Then submitted to NPC block for parsing and then MCAM lookup to get the destination RVU device.
- NIX LF attached to the destination RVU device allocates a buffer from RQ mapped buffer pool of NPA block LF.
- RQ may be selected by RSS or by configuring MCAM rule with a RQ number.
- Packet is DMA’ed and driver is notified.
Egress¶
- Driver prepares a send descriptor and submits to SQ for transmission.
- The SQ is already configured (by AF) to transmit on a specific link/channel.
- The SQ descriptor ring is maintained in buffers allocated from SQ mapped pool of NPA block LF.
- NIX block transmits the pkt on the designated channel.
- NPC MCAM entries can be installed to divert pkt onto a different channel.
Devlink health reporters¶
NPA Reporters¶
Drivers Marvell Port Devices Replicator
The NPA reporters are responsible for reporting and recovering the following group of errors:
- GENERAL events
- Error due to operation of unmapped PF.
- Error due to disabled alloc/free for other HW blocks (NIX, SSO, TIM, DPI and AURA).
- ERROR events
- Fault due to NPA_AQ_INST_S read or NPA_AQ_RES_S write.
- AQ Doorbell Error.
- RAS events
- RAS Error Reporting for NPA_AQ_INST_S/NPA_AQ_RES_S.
- RVU events
- Error due to unmapped slot.
Sample Output:
Each reporter dumps the
- Error Type
- Error Register value
- Reason in words
Drivers Marvell Port Devices Gigabit
For example:
